Storage Tanks Internal Cathodic Protection
The internal corrosion of the aboveground tanks is one of the problems that causes many damages to the oil and gas industry annually. Tanks Internal cathodic protection is used as a complementary coating or sometimes independent method to prevent corrosion.
The type and thickness of coatings used in aboveground tanks is particularly important and determines the amount of cathodic protection required current. Aboveground tanks internal cathodic protection is done by two methods of sacrificial anode and impressed current, which is the most common method of sacrificial anode. In the sacrificial anode cathodic protection method, depending on the type of electrolyte, its resistivity, the flammability or non-flammability of the electrolyte, aluminum, zinc and magnesium anodes are used. According to some technical literature, such as the Iranian Petroleum Standard, zinc anodes can only be used in electrolytes that are flammable because otherwise sparks and explosions are likely. It has been recommended that high potential magnesium anodes or hygienically approved alloys be used in drinking water tanks because the ions released from aluminum and zinc anodes are extremely detrimental to health.
Schematic of aboveground tanks internal cathodic protection by of sacrificial anode method
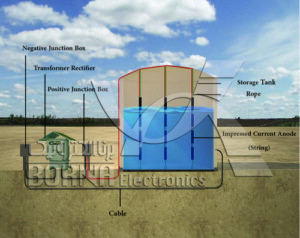
Schematic of aboveground tanks internal cathodic protection by of impressed current method
Borna Electronics Co. with over 30 years of experience in cathodic protection, declares its readiness to design, procurement, consultation and construction of cathodic protection systems for aboveground tanks internal and implement cathodic protection monitoring systems for them.