Magnesium anodes
Magnesium anodes are the most common sacrificial anodes used for the protection of buried structures in the soil, such as oil and gas pipelines, bottom and external body of storage tanks. Magnesium anodes are also used for the internal protection of water heaters and water tanks, heat exchangers, condensers and other structures that are in contact with water and operate at high temperatures.
Magnesium anodes are divided into two categories in terms of chemical composition and type of application:
A) Standard magnesium anodes (AZ63)
B) High potential magnesium anodes (M1C)
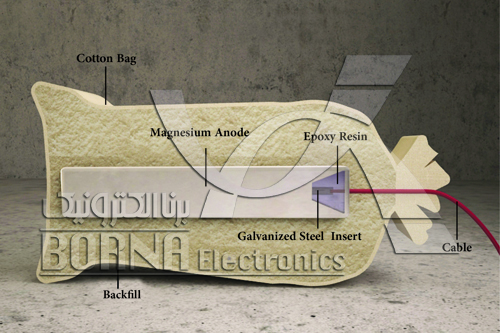
Schematic of magnesium anode with a backfill used in soil and its components
Magnesium anodes with backfill manufactured by Borna Electronics Co. used in soil
Magnesium anodes manufactured by Borna Electronics Co. used in heat exchangers
Common standards for magnesium anodes include ASTM B843, ASTM G97, IPS-M-TP-750 and NACE SP0387. According to NACE SP0387 standard, the insert used in magnesium anodes shall be of galvanized steel.
Chemical composition of magnesium anodes according to ASTM B438 standard
|
Element (Wt%) |
Chemical composition |
|
|
Standard alloy |
High potential alloy |
|
|
Aluminum |
5.3-6.7 |
0.01 Max. |
|
Zinc |
2.5-3.5 |
– |
|
Manganese |
0.15-0.7 |
0.5-1.3 |
|
Silicon |
0.10 Max. |
0.05 Max. |
|
Copper |
0.02 Max. |
0.02 Max. |
|
Nickel |
0.002 Max. |
0.001 Max. |
|
Iron |
0.003 Max. |
0.03 Max. |
|
Other elements |
0.30 Max. |
0.30 Max. |
|
Magnesium |
Reminder |
Reminder |
Electrochemical properties of zinc anodes according to DNV-RP-B401 standard
|
Electrochemical properties |
Standard alloy |
High potential alloy |
|
Electrochemical capacity (A.h/kg) |
1200 Min. |
1200 Min. |
|
Closed circuit potential (V vs Ag/AgCl) |
-1.5 Max. |
-1.7 Max. |
|
Efficiency (%) |
60 Min. |
50 Min. |
For the cathodic protection of buried structures in the soil, it is necessary to use backfill around the anode. The duties of the backfill materials are:
- Anode potential stability
- Prevent anode polarization
- Reduced resistance between anode and soil and increased anode output current
- Creates uniform corrosion at the anode, reducing the anode’s self-corrosion and increasing its efficiency
The backfill material is usually a mixture of gypsum, bentonite, and sodium sulphate.
- The backfill compound (A) is suitable in areas with low soil moisture because bentonite in it has water retention properties.
- The backfill compound (B) is commonly used for zinc anodes.
- The backfill compound (C) is suitable for magnesium and zinc anodes in very moist and marshy soils because it holds well around the anode.
- The backfill compound (D) has low resistivity and is suitable for areas with high soil resistivity to reduce resistance between the anode and the ground.
Different chemical composition of sacrificial anodes backfill used in soil according to IPS-M-TP-750 standard
|
Backfill type |
Gypsum% (CaSO4) |
Bentonite% |
Sodium Sulphate% |
Approximate resistivity (ohm.cm) |
|
|
Hydrated |
Molding Plaster |
||||
|
A |
25 |
– |
75 |
– |
250 |
|
B |
50 |
– |
50 |
– |
250 |
|
C |
– |
50 |
50 |
– |
250 |
|
D |
75 |
– |
25 |
5 |
50 |
According to IPS-M-TP-750 standard, the grading of the backfill material shall be such that 100% of the particles pass through the sieve with 0.84 mm holes (mesh 20) and 50% of its particles remain on sieve with 0.15 mm holes (100 mesh). Also, the moisture content of the backfill shall not exceed 5% (if the moisture content of the backfill is high, the anode will corrode during storage).
The anode shall be placed in the center of the backfill and the soil around the backfill should be firmly pressed. After installing the anode and pouring the soil on it and before the pit is fully filled, It should be poured over the landfill of the anode. The anode backfill absorbs sufficient moisture after 3 weeks and the anodes reach steady state and have maximum output current.
If the anode is not packaged, the backfill is manually dumped around it. The backfill should be laid dry around the anode. Once the backfill is complete and Pour the soil on it before the pit is completely filled, like packaged anodes, water must be poured into the pit.
The backing material is such that it expands with water absorption. This will make the backfill better connected to the soil around it. If the backfill is mixed with water and flushed around the anode, there may be a hole in the backfill after losing the extra backfill water which will reduce the outflow of the anode.
Borna Electronics Co. declares its readiness to design and manufacture all types of magnesim anodes based on the requests of respected clients or project needs.